Newton's 2nd Law: Rotation
The relationship between the net external torque and the angular acceleration is of the same form as Newton's second law and is sometimes called Newton's second law for rotation. It is not as general a relationship as the linear one because the moment of inertia is not strictly a scalar quantity. The rotational equation is limited to rotation about a single principal axis, which in simple cases is an axis of symmetry.
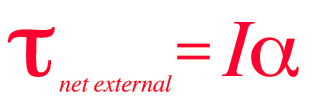
Net external torque = moment of inertia x angular acceleration
Moment of inertia concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics ***** Rotation | R Nave |