Neutrino Transparency Temperature
In evaluating the energy density in the background radiation in the universe, it is necessary to include both the photon 3K background and the neutrino background. The neutrino transparency point occurred before the photon transparency which gives us the microwave background radiation. In estimating that transparency temperature for neutrinos, Weinberg uses an entropy argument.
Presuming that the expanding universe did so under conditions of thermal equilibrium, the second law of thermodyamics suggests that entropy remained constant. The entropy per unit volume at temperature T can be approximated by
S α NTT3
where NT is the effective number of species in thermal equilibrium . This includes only those particles which have a critical temperature less than T, i.e., they can be formed from the current level of thermal energy. To keep the entropy constant for an expanding universe, the entropy must be proportional to the inverse cube of the volume so that
SR3 α NTT3R3 = constant
where R can be taken to be the separation between typical particles.
After the neutrinos in the early universe went out of equilibrium, only electrons, positrons and photons were left in thermal equilibrium, and that changed with the annihilation of the electrons and positrons at about 5 x 109K. To evaluate the effect on the temperature, one must examine the number of species which goes into the entropy expression. The effective numbers are:
|
| The effective numbers for the particles are calculated as the product of the three factors:
|
So with the electron-positron annihilation, the effective numbers changed.
| Nbefore = 7/2 + 2 | Nafter = 2 |
By the constancy of entropy:
The energy release of the electron-positron annihilation changes the quantity TR by the factor:
This is the factor which allows us to calculate the effective temperature of the neutrino background. We reason that before the electron-positron annihilation, the temperature for the photons and neutrinos was the same. Since the neutrinos had decoupled at that time, the product TνR for the neutrinos remains equal to the product TeR before the annihilation. For the present universe this gives
for the effective temperature of the neutrino background.
The amount of energy in this neutrino background can be estimated with the use of the Stefan- Boltzmann law, treating the neutrinos as massless particles at 1.9K. The ratio of the neutrino energy density in this equilibrium radiation can be expressed as a fraction of the photon energy density of about 0.25 MeV/m3
We used the fact that the neutrinos are more numerous by the factor (7/2)/2 =7/4, there being a factor of 2 for the effective number of photons because of two polarization states. The combined energy density in the background radiation is then
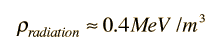
| Relate to temperature and expansion time |
Reference
Weinberg
First 3 Minutes
| HyperPhysics***** Astrophysics | R Nave |