Virtual Image Formation
Converging lenses form virtual images if the object distance is shorter than the focal length. Using the common form of the lens equation, i is negative. Such images are formed with the simple magnifier .
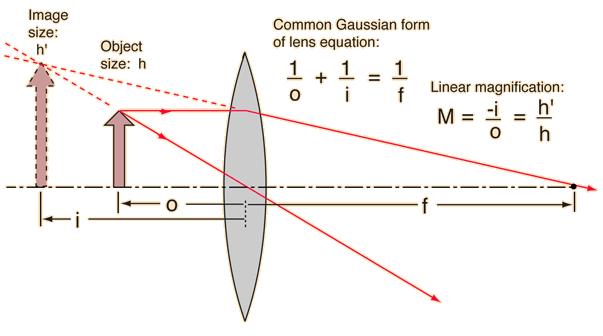
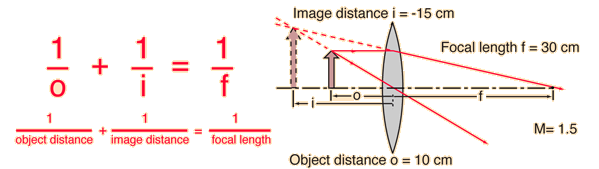
If an object distance smaller than the focal length is entered to agree with the illustration, then the image is an enlarged virtual image on the same side of the lens as the object and will give a negative image distance. If a calculation yields a negative focal length, then the lens is a diverging lens rather than the converging lens in the illustration. The lens equation can be used to calculate the image distance for either real or virtual images and for either positive on negative lenses. The linear magnification relationship allows you to predict the size of the image.
| Other ways to form virtual images |
Lens concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |