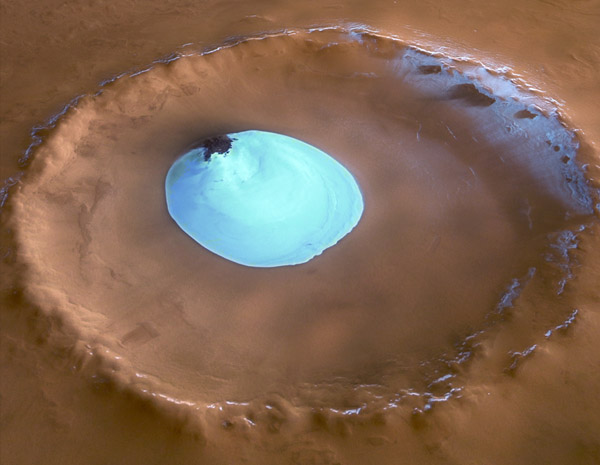
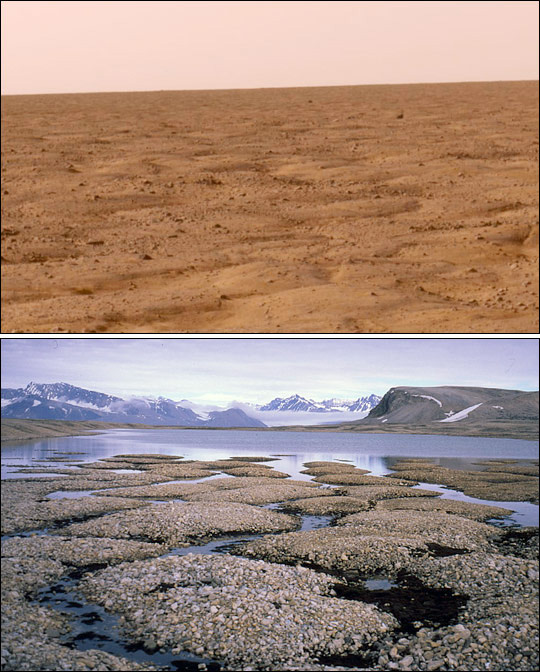
Runoff Channels on Mars
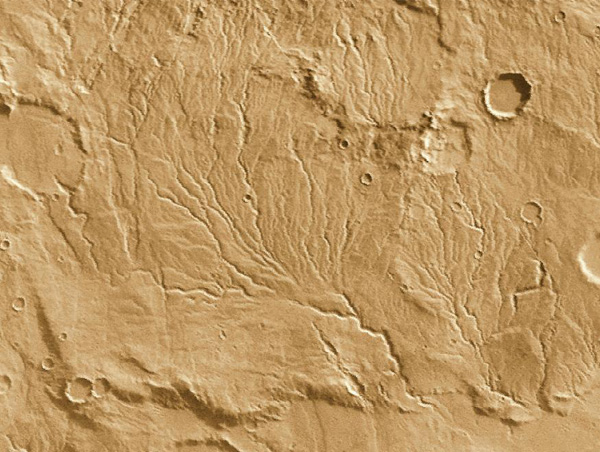

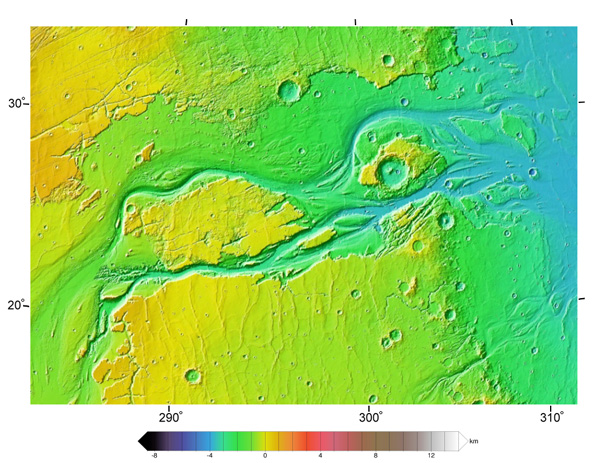
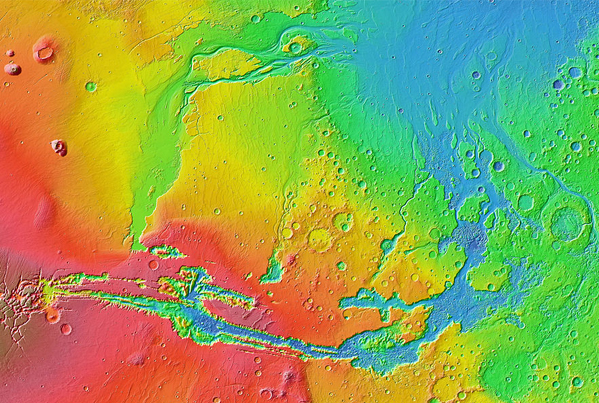
In the highland plains of Mars in the equatorial region there are many small channels which look like the runoff channels which carry water from rainstorms. These channels are typically a few meters deep, tens of meters wide and some 10 to 20 km long. These runoff channels are part of the evidence that Mars had much surface water at a previous period of its history.
Some indication of the age of a feature can be obtained from counting craters. The crater density in the runoff areas is greater than the lunar maria but less than the lunar highlands. Lunar maria dates extend back to 3.9 billion years, so the implied age of the runoff channels is somewhat older than that.
The runoff channels are much smaller than the apparently younger outflow channels.
There are no runoff channels in the northern plains, which are dated at more than 3 billion years old, so it has been a long drought - no rain for over 3 billion years. The conditions which gave runoff channels required a much more dense atmosphere than the present one, so the rough chronology that one can get from crater counting tells us something about when the atmosphere was lost.
Mars Concepts
Solar System Illustration
Solar System Concepts
Reference
Fraknoi, Morrison, Wolff
Ch 9
| HyperPhysics********** Astrophysics | R Nave |