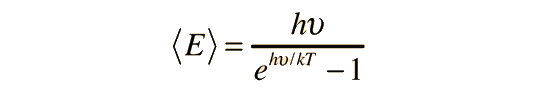Einstein's Contribution to Specific Heat Theory
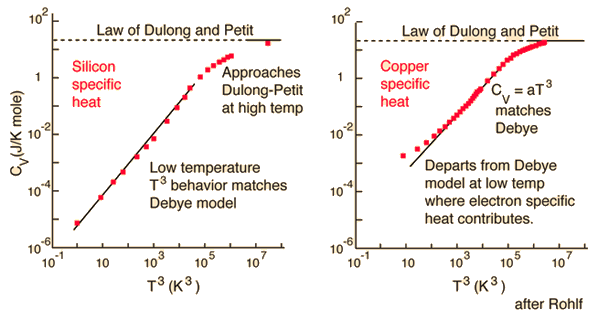
The Law of Dulong and Petit assumed that Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics and equipartition of energy could be applied even at low temperatures. Einstein recognized that for a quantum harmonic oscillator at energies less than kT, the Einstein-Bose statistics must be applied. This was the same conclusion that was drawn about blackbody radiation. The statistical distribution of energy in the vibrational states gives average energy:
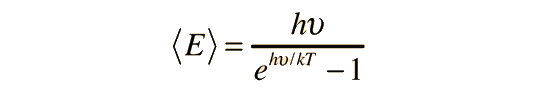
where this frequency is the frequency of a quantum vibrator. There are three degrees of freedom per vibrator, so the total energy is

The derivative of this gives:

For high temperatures, this expression approaches agreement with the Law of Dulong and Petit. |
|
In the Einstein treatment, the appropriate frequency in the expression had to be determined empirically by comparison with experiment for each element. The quantity hu/k is sometimes called the Einstein temperature. Although the general match with experiment was reasonable, it was not exact. Debye advanced the treatment by treating the quantum oscillators as collective modes in the solid which are now called "phonons".
|