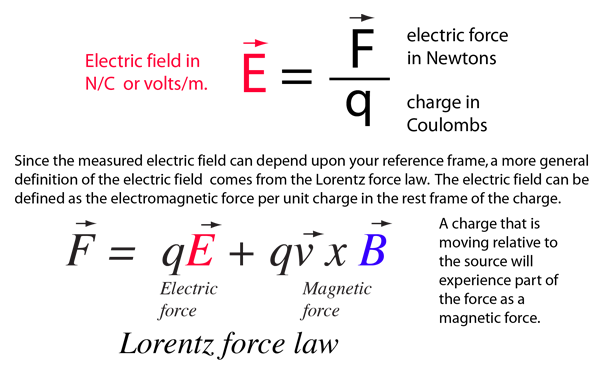
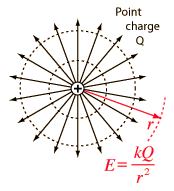
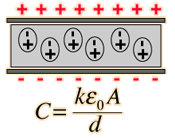
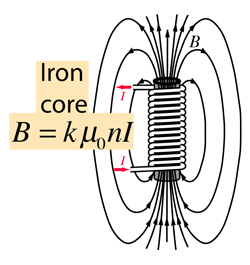
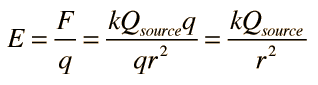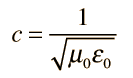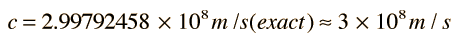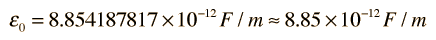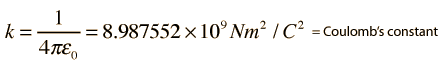Electric and Magnetic Constants
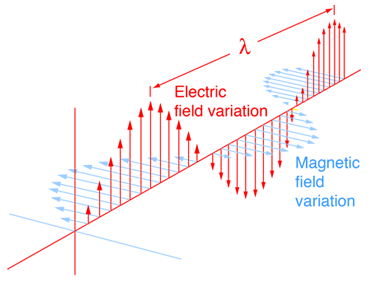
In the equations describing electric and magnetic fields and their propagation, three constants are normally used. One is the speed of light c, and the other two are the electric permittivity of free space ε0 and the magnetic permeability of free space, μ0. The magnetic permeability of free space is taken to have the exact value
This contains the force unit N for Newton and the unit A is the Ampere, the unit of electric current.
With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship
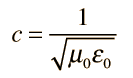
where the speed of light c is given by
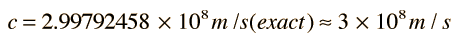
This gives a value of free space permittivity
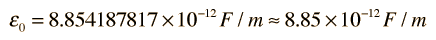 which in practice is often used in the form
which in practice is often used in the form
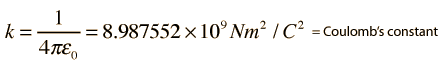
These expressions contain the units F for Farad, the unit of capacitance, and C for Coulomb, the unit of electric charge.
In the presence of polarizable or magnetic media, the effective constants will have different values. In the case of a polarizable medium, called a dielectric, the comparison is stated as a relative permittivity or a dielectric constant. In the case of magnetic media, the relative permeability may be stated.
|
Index
Electric field concepts |