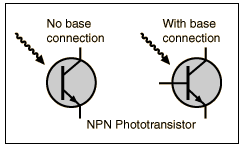
Photoresistors
Low cost, two lead photoresistors using a cadmium sulfide (CdS) element show a dramatic decrease in resistance when illuminated and are commonly used as a light sensing element for security lights, etc. so that they will turn on at night. In the dark, the resistance is very high, in the 1 megohm range. When illuminated, the resistance may drop to a few hundred ohms. They are typically more sensitive to green light, and they have a very high sensitivity compared to other types of sensors. They cannot be practically used for high speed switching or modulation for communications purposes because there is a "memory effect", requiring on the order of a second for the resistance to rise to its dark resistance.
Electronics concepts
Optoelectronics concepts
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |