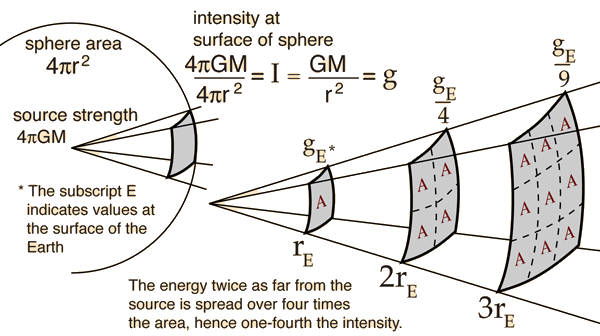
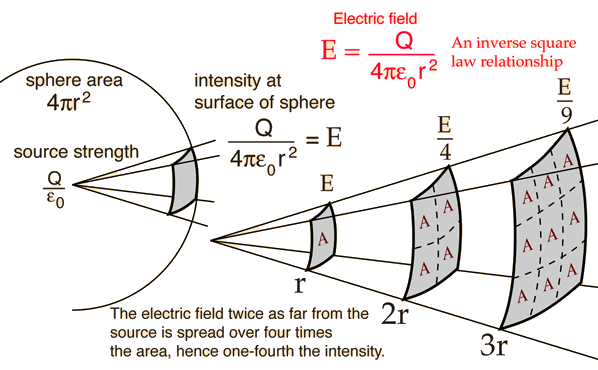
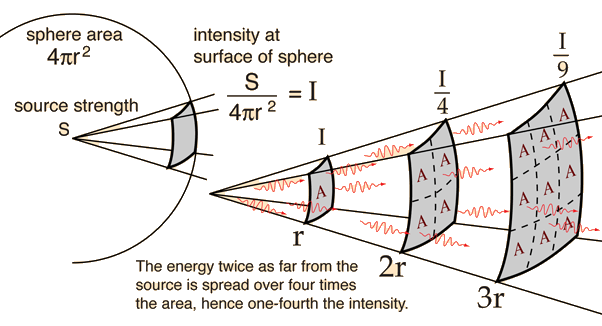
Inverse Square Law, General
Any point source which spreads its influence equally in all directions without a limit to its range will obey the inverse square law. This comes from strictly geometrical considerations. The intensity of the influence at any given radius r is the source strength divided by the area of the sphere. Being strictly geometric in its origin, the inverse square law applies to diverse phenomena. Point sources of gravitational force, electric field, light, sound or radiation obey the inverse square law. It is a subject of continuing debate with a source such as a skunk on top of a flag pole; will its smell drop off according to the inverse square law?
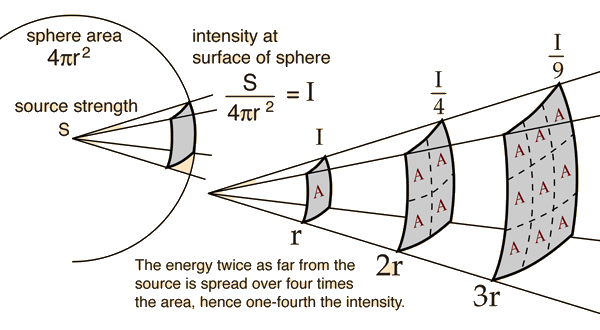
Applications of the inverse square law:
| Gravity | Electric field | Light | Sound | Radiation |
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |