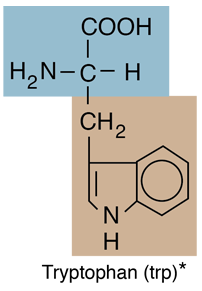
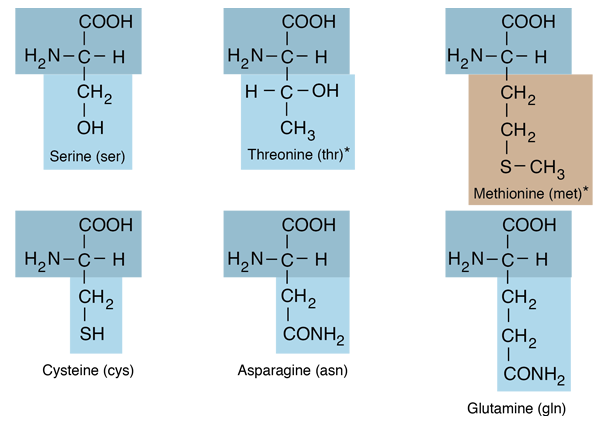
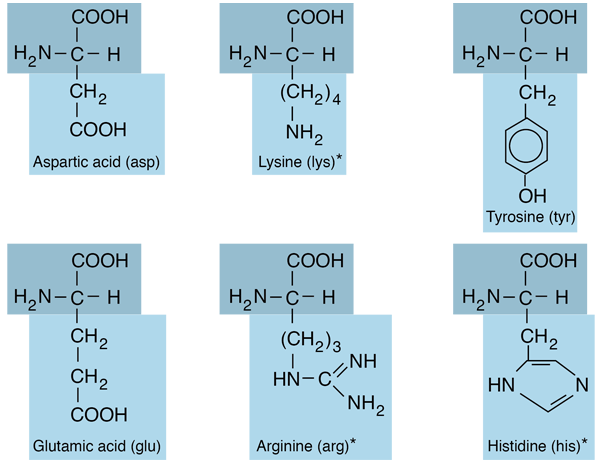
Amino Acids with Hydrocarbon R-groups
Amino acids are organic compounds which contain both an amino group and a carboxyl group. They are distinguished by the attached functional group R.
 |
Of the twenty amino acids that make up proteins, six of them have hydrocarbon R-groups . Except for phenylalanine, these are aliphatic hydrocarbons, containing no benzine ring. The simplest of the amino acids, glycine, has just a hydrogen atom in the position of the R-group. |
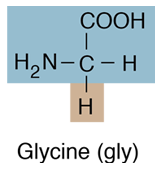 |
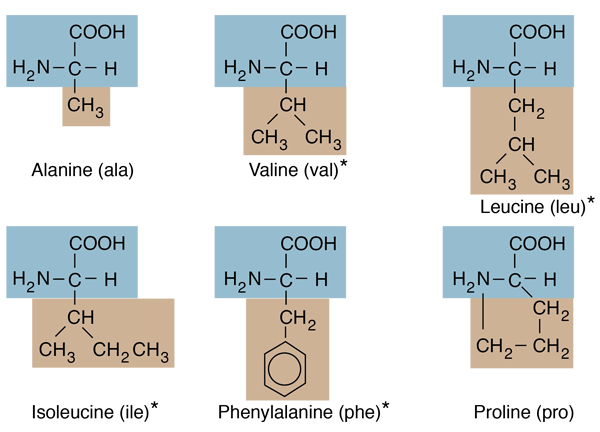
* Amino acids which are essential amino acids which cannot be made by the human body and, therefore, must be obtained in the diet.
Amino acids may be characterized in various ways. Important to the structure of proteins is whether they are hydrophobic or hydrophilic. These amino acids are for the most part hydrophobic. For details about the ways to classify amino acids, see the IMGT classes for amino acids.
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Tillery, Enger and Ross
Ch 14
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |