The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP)
The WMAP mission provided the first detailed full-sky map of the microwave background radiation in the universe. The map produced is characterized as a map of the effective temperature of the microwave background radiation as depicted below. The later Planck satellite refined that map.
This is a synopsis of the description of the mission from the WMAP mission report on the NASA website. The illustrations are NASA graphics.
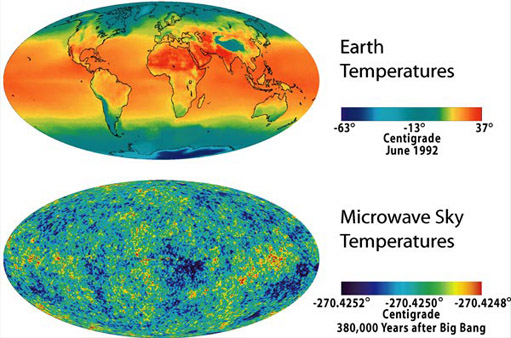
Note that the temperature variation on the Earth covers about 100°C while those measured by WMAP range only over about 0.0004 °C, a smaller range by a factor of a quarter of a million.
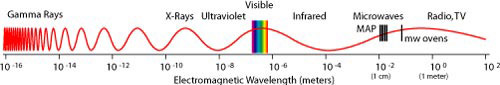
The wavelengths of radiation detected by WMAP were in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum as depicted in the NASA graphic below.
The synopsis of the implications of WMAP as summarized in the mission report includes the following quote from the WMAP site:
- Universe is 13.7 billion years old, with a margin of error close to 1%.
- First stars ignited 200 million years after the Big Bang.
- Light in WMAP picture is from 379,000 years after the Big Bang.
- Content of the Universe:
- 4% Atoms, 23% Cold Dark Matter, 73% Dark Energy.
- The data places new constraints on the Dark Energy. It seems more like a "cosmological constant" than a negative-pressure energy field called "quintessence". But quintessence is not ruled out.
- Fast moving neutrinos do not play any major role in the evolution of structure in the universe. They would have prevented the early clumping of gas in the universe, delaying the emergence of the first stars, in conflict with the new WMAP data.
- Expansion rate (Hubble constant) value: H0 = 71 km/sec/Mpc (with a margin of error of about 5%.
- New evidence for Inflation (in polarized signal).
- For the model which fits our data, the Universe will expand forever. The density parameter Ω is measured to be 1.02 +/- 0.02 . (The nature of the dark energy is still a mystery. If it changes with time, or if other unknown and unexpected things happen in the universe, this conclusion could change.)
The positioning of the WMAP satellite made use of the Earth-Sun Lagrange point L2 which permitted it to be kept in place with a minimum expenditure of fuel and always keep its sensors pointed away from both the Earth and the Sun.
| Early universe chronology |
| Age of the universe |
References

WMAP home page
| HyperPhysics***** Astrophysics | R Nave |