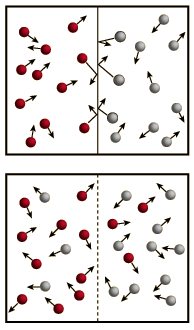
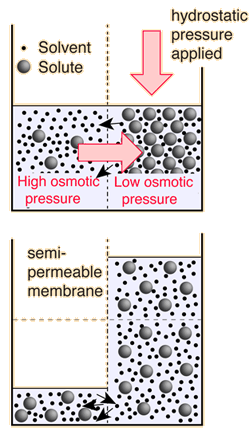
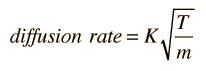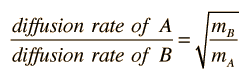Osmotic Pressure
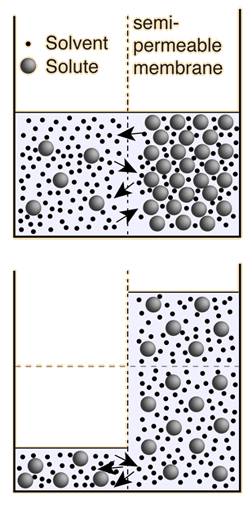
Osmosis is a selective diffusion process driven by the internal energy of the solvent molecules. It is convenient to express the available energy per unit volume in terms of "osmotic pressure". It is customary to express this tendency toward solvent transport in pressure units relative to the pure solvent.
If pure water were on both sides of the membrane, the osmotic pressure difference would be zero. But if normal human blood were on the right side of the membrane, the osmotic pressure would be about seven atmospheres!
This illustrates how potent the influence of osmotic pressure is for membrane transport in living organisms.
|
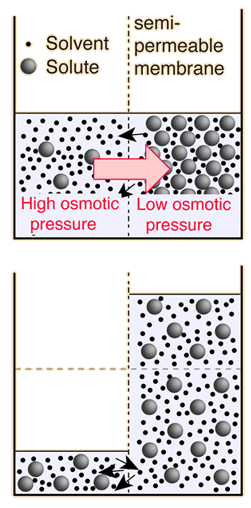
The decision about which side of the membrane to call "high" osmotic pressure is a troublesome one. The choice made here is the opposite of that made in many biology texts, which attribute "high" osmotic pressure to the solution and zero osmotic pressure to pure water. The rationale for the choice is that the energy which drives the fluid transfer is the thermal energy of the water molecules, and that energy density is higher in the pure solvent since there are more water molecules. The thermal energy of the solute molecules does not contribute to transport, presuming that the membrane is impermeable to them. The choice is also influenced by the observed direction of fluid movement, since under this choice the fluid transport is from high "pressure" to low, congruent with normal fluid flow through pipes from high pressure to low. The final rationale has to do with the measurement of osmotic pressure by determining how much hydrostatic pressure on the solution is required to prevent the transport of water from a pure source across a semi-permeable membrane into the soluton. A positive pressure must be exerted on the solution to prevent osmotic transport, again congruent with the concept that the osmotic pressure of the pure solvent is relatively "high".
Nevertheless, the dialog continues on this issue since the discussion of osmosis is most relevant to the biological and life sciences and perhaps the logic stated above should yield to the conventions of the field in which the phenomena are most relevant.
|
|
|
Index
Kinetic theory concepts
Applications of kinetic theory
Fluid concepts |