|
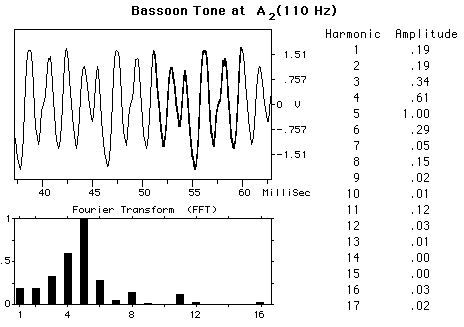
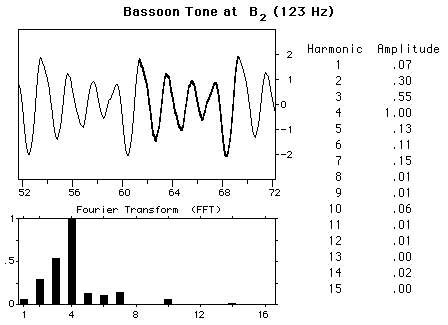
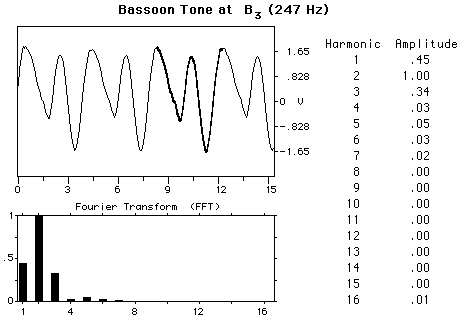
The BassoonThe bassoon is a double-reed woodwind instrument with a conical bore air column, the bass member of the oboe family. Its normal range is about 3 octaves, from B1flat to E5flat. The tube, 2.79 m (9 ft 2 in) long, is bent to make a height of 1.22 m (4 ft) and consists of a metal crook on which the reed is placed and four sections of maple or pearwood: the tenor, the butt, the bass, and the bell. The characteristic sound of a bassoon is influenced by a strong formant, as illustrated by the accompanying waveforms. Each of the notes displayed has a peak of intensity in the neighborhood of 500 Hz. The double reed is made from cane, with most bassoonists making their own reeds. The player's lips exert a lot of control over the reed, with more than half of the reed in the player's mouth. The player's left hand is responsible for seventeen different keys with nine of them controlled by the thumb. The right hand controls twelve with four for the thumb.
|
Woodwind instruments
Musical instruments
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |