Holmes-Houtermans System for Lead Isochrons
The lead-lead isochron method for determining the age of ancient rocks including meteorites is generally thought to be the most reliable and precise method for such dating. Dalrymple calls the lead method "the hourglass of the solar system". Many years of painstaking research has gone into establishing what is commonly called the Holmes-Houtermans System.

This approach to Pb-Pb isochrons makes use of two of the natural radioactive series, the uranium-238 series and the uranium-235 series, which are related to each other by the fact that the isotopic ratio 238U = 137.88235U has been found to be consistent for Earth, moon and meteor rocks. The two series proceed to different final lead isotopes:
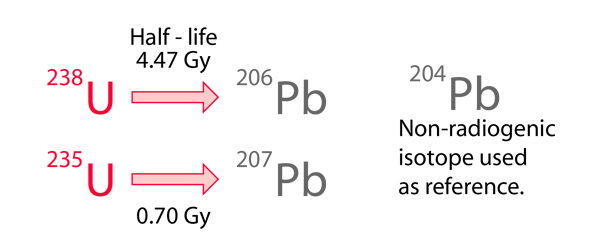
The development of the Holmes-Houtermans approach follows the basics of radioactive decay acting as a clock. Even though the decay of 238U to 206Pb goes through about 14 steps, it all eventually reaches that endpoint and may be reasonably characterized by an effective halflife of 4.47 Gy.
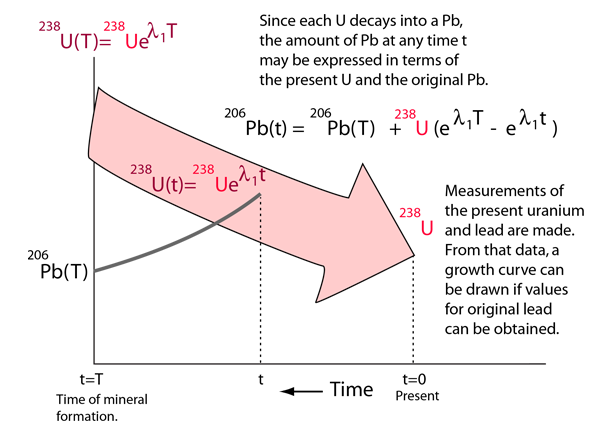
Since the present values of uranium and lead are measured, it is customary to let the clock run backward and model the process as an exponential increase of uranium. Since the 204Pb is used as a standard, all quantities are expressed as ratios to the 204Pb content. A growth curve for the 206Pb can then be developed, based on the experimental 238U content.
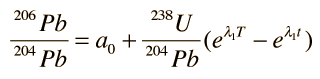
The process is the same for 235U , yielding the growth curve for 207Pb
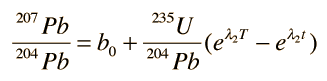
In these growth curves of the lead isotopic ratios with time, a0 and b0 are the lead isotopic ratios at the time of formation T:
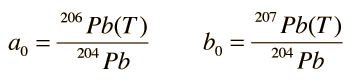
and λ1 and λ2 are the decay constants for 238U and 235U respectively.
While growth curves as a function of time may be useful, it is more advantageous to plot growth curves in terms of the isotopic ratios 207Pb/204Pb versus 206Pb/204Pb. This is made possible by the fact that the isotopic ratio of the uranium isotopes is consistent in rocks from the Earth, moon and meteorites and can be used to couple the growth curves above. Using this ratio
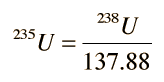
the growth curve for 207Pb above can be written
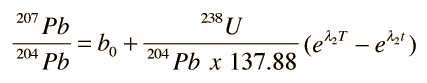 .
.This couples the time-growth equations and permits the plotting of a growth curve in terms of the lead isotope ratios instead of time, as shown in the top illustration. Different growth curves are obtained for different uranium content. The uranium content is denoted by the symbol μ and the growth curves in the top illustration show that curves with higher values of μ give higher curves on that kind of plot.
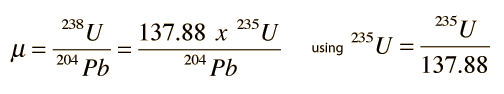
If you have a given rock sample with several distinct minerals within it, there will in general be a variety of values of μ and therefore several different growth curves. The final conceptual step in the Holmes-Houtermans system is then to note that a ratio of the growth equations for the two radiogenic lead isotopes gives a relationship which is independent of the uranium content μ and gives the equation of a straight line, an isochron.
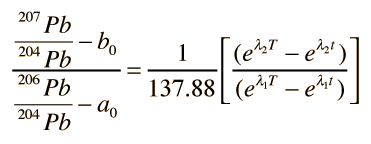
Again referring to the top illustration, if you put in a value of time t, a straight line is produced which will cross the growth curves for the different μ values. If you put in t=0, representing the present time, then you get the present isochron in that illustration. The slope of the present isochron gives the value T of the formation of the rock from a molten state. The equation for the age T is transcendental and cannot be solved directly, but it can be solved graphically or by successive approximations.
The remaining great challenge to using Pb-Pb isochrons to determine the age of rocks was the determination of the primeval ratios of the lead isotopes, a0 and b0, since they are necessary to determine the slope of the present isochron. A number of years of experimentation has established the link between the oldest Earth rocks and meteorites, and it appears that meteorites form the best references for determining a0 and b0. In particular, the troilite mineral from the Canyon Diablo meteorite has shown the lowest original uranium content and is typically used as the standard for determining the original concentrations.
The values for a0 and b0 are from Tatsumoto, Knight and Allegre, 1973. The other values are earlier values from Patterson. Dalrymple describes the Tatsumoto, et al result as "the generally accepted value for primeval lead in the solar system."
| Pb-Pb isochron referencing Canyon Diablo |
| Meteorite dating | Clocks in the rocks |
References
Patterson
Dalrymple
Tatsumoto, et al
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | R Nave |