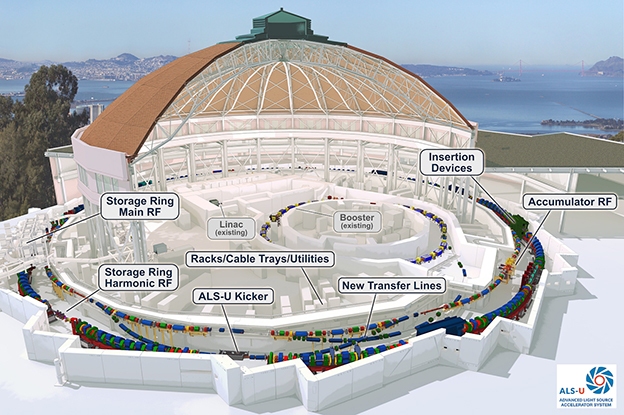
SLAC
The Stanford Linear Accelerator Center has a 2 mile linear accelerator. In a single pass, it accelerates electrons to 25 GeV. In one configuration it feeds electrons and positrons into the SPEAR colliding beam storage rings.The Stanford Positron Electron Accelerator Rings (SPEAR) is notable for the discovery of the charm quark and the tau lepton. By achieving full acceleration for electrons and positrons in opposite directions, it can achieve 50 GeV of energy for colliding beam experiments. This energy corresponds to the electron traveling at a speed within 2 cm/s of the speed of light (Ohanian).
Electrons are accelerated to 30 MeV before injection into the main accelerator. Electromagnetic waves are generated by 245 microwave oscillators (klystrons) operating at a power of 67 megawatts apiece (Blatt)!
See schematic on p412 of Blatt's Modern Physics
| Some discoveries at SLAC |
|
| Accelerators |
Particle concepts
Search for elementary particles
References
Blatt
Ch 16
Ohanian
Ch 46

SLAC
| HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics | R Nave |