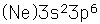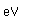Argon
Argon is a noble gas which composes about 1% of the atmosphere. It is used in incandescent light bulbs to permit the filament to be heated to a higher temperature, and therefore to produce a whiter light than would be practical in a vacuum. The argon decreases the rate at which the tungsten filament evaporates by hindering the diffusion of the vaporized metal atoms away from the filament, increasing the probability that they will reattach to the filament.
Argon is used for producing gas lasers which produce green light.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 5 |