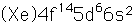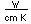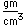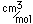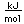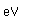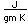Osmium
Osmium is an iron-gray metal, a member of the platinum group. Osmium forms the oxide OsO4 called osmic acid. It is a white crystalline powder which melts at 40°C and boils at about 100°C. It has a strong odor reminiscent of chlorine and is very poisonous. It can be reduced by organic matter and is used for staining of histological samples for microscope viewing. The reduction produces a metallic osmium structure which images the sample without distorting it.
Osmium has the distinction of being the most dense of all the naturally occuring elements at 22.57 gm/cm^3. This is almost twice the density of lead at 11.4 gm/cm^3.
Osmium is often associated with ruthenium.
|