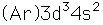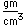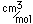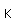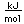Vanadium
Vanadium is classified as a transition metal and is the most important in its group (called the Vanadium group). It finds extensive use in the manufacture of special steels with exceptional strength and toughness. One use is for the manufacture of automobile crankshafts.
It occurs naturally in the mineral vanadinite. It is also found in the silicate mineral cavansite. An oxide with zinc and lead is descloizite. Vanadium appears with uranium and lead in Francevillite. An oxide of copper with vanadium is volborthite. An oxide of vanadium with zinc, copper and lead is mottramite.
|