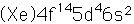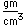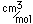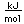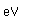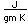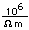Tungsten
Tungsten is a strong, heavy metal with an extremely high melting point (3370°C). It is used for the filaments of light bulbs, the electric contacts in spark plugs, and as electron targets in x-ray tubes.
Alloyed with steel (tungsten steel) it retains its hardness even when hot, making it valuable for high speed cutting tools. Tungsten carbide (WC) is used for the cutting edges of high speed tools.
Tungsten is also called wolfram, the origin of the chemical symbol (W).
Tungsten-containing oxide minerals are ferberite, scheelite and Hubnerite. An oxide of tungsten with lead is stolzite. An oxide of tungsten with iron and manganese is Wolframite.
|