Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an experimental technique for obtaining emission or absorption spectra of materials (solids, liquids, or gases). By spectra, one means a measurement of emission or absorption intensity as a function of frequency or wavelength. But instead of finding the spectrum by sweeping a monochromatic radiation source through a frequency range, this technique irradiates the material to be studied with a broad band of frequencies simultaneously and then performs a mathematical Fourier transform to calculate the distribution of the signal as a function of frequency. Perhaps a useful visualization of the idea is the application of Fourier analysis to convert from a time display of sound to a display of intensity as a function of frequency for sound analysis.
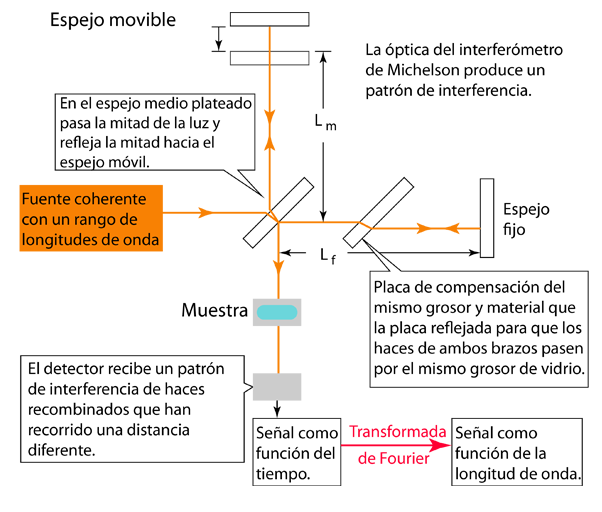
Using FTIR to obtain the infrared absorption spectrum of a material usually involves illuminating the sample with a broad band of frequencies to obtain a distribution of intensity vs position in an image plane and then repeating the process rapidly while changing the position of a mirror in a scanning Michelson interferometer. Each position produces a unique interference pattern. The collection of these interference patterns as a funtion of time can be mathematically converted by the Fourier transform calculation into a distribution of absorption intensity as a function of wavelength.
|
|
Molecular spectra concepts
References
FTIR Wiki
mks-Newport, Technical Note
| HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics | R Nave |