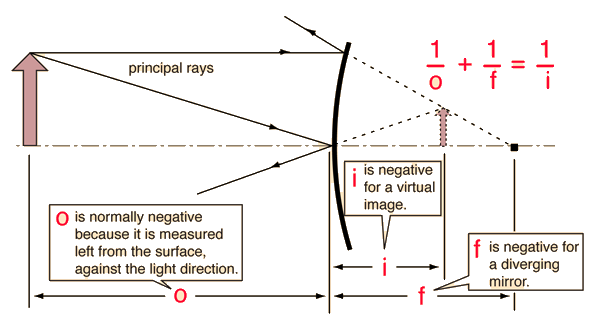
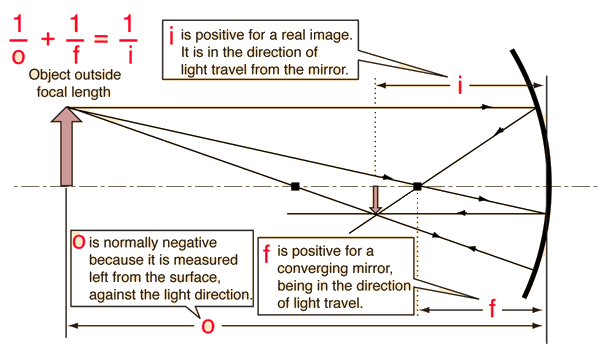
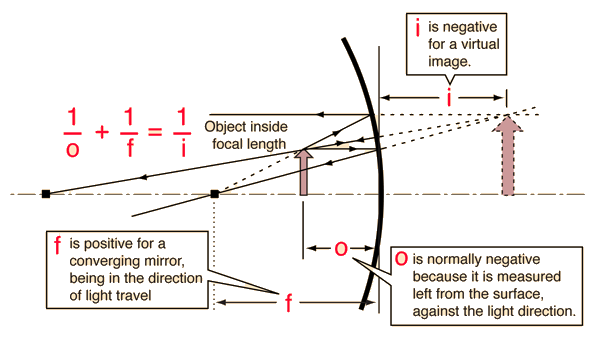
Mirror Ray Tracing
Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and retraces its path backward.
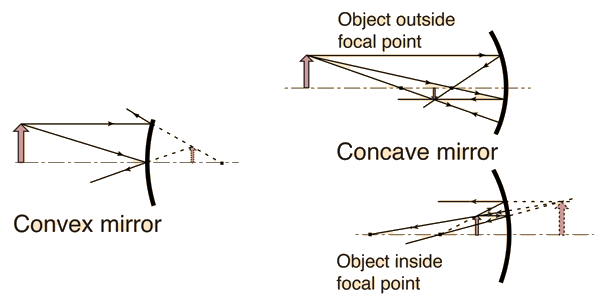
Mirror concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |