Ear and Hearing
Hearing concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |
Ear and Hearing |
Index Hearing concepts | ||
|
Go Back |
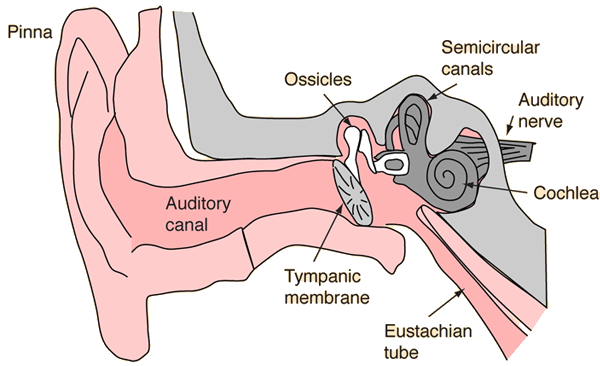
The Outer EarSound energy spreads out from its sources. For a point source of sound, it spreads out according to the inverse square law. For a given sound intensity, a larger ear captures more of the wave and hence more sound energy. The outer ear structures act as part of the ear's preamplifier to enhance the sensitivity of hearing. 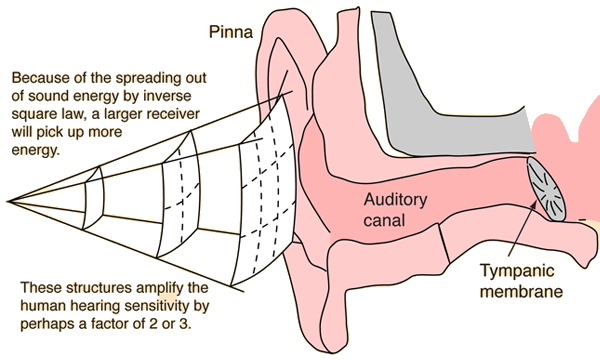 The auditory canal acts as a closed tube resonator, enhancing sounds in the range 2-5 kiloHertz. |
Index Hearing concepts | ||
|
Go Back |
The Tympanic MembraneThe tympanic membrane or "eardrum" receives vibrations traveling up the auditory canal and transfers them through the tiny ossicles to the oval window, the port into the inner ear.
|
Index Hearing concepts Zemlin Clark & Martin | ||
|
Go Back |