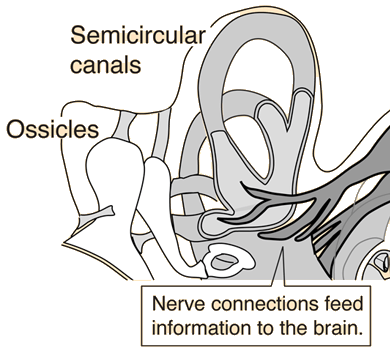
The Inner Ear
The small bone called the stirrup, one of the ossicles, exerts force on a thin membrane called the oval window, transmitting sound pressure information into the inner ear.
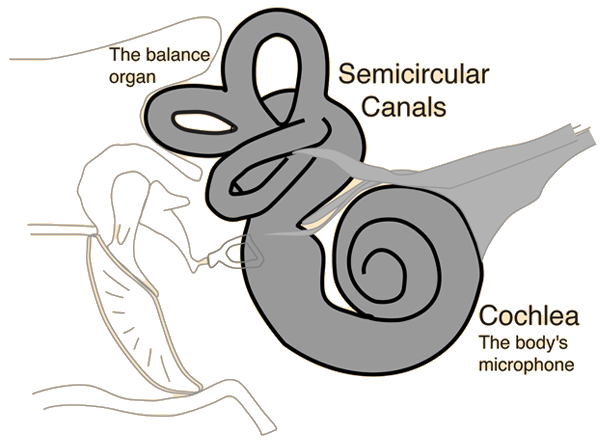
The inner ear can be thought of as two organs: the semicircular canals which serve as the body's balance organ and the cochlea which serves as the body's microphone, converting sound pressure impulses from the outer ear into electrical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve.
The basilar membrane of the inner ear plays a critical role in the perception of pitch according to the place theory.
Hearing concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |