DC Parallel Circuit
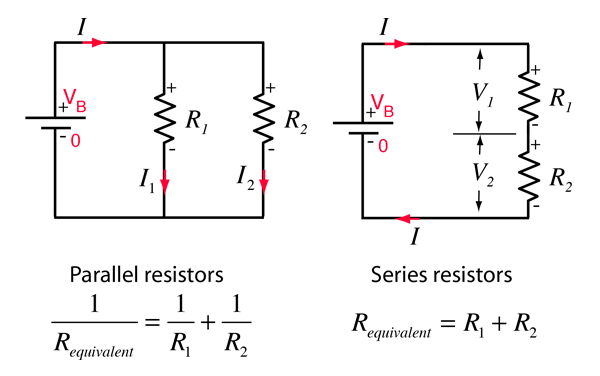
Comparison of parallel and series circuits with the same resistors and the same battery voltage applied.
| DC circuit examples | Resistor combinations |
| Batteries and bulbs example |
| Bulbs in series and parallel |
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |