Electric Quadrupole Moments of Nuclei
The nuclear electric quadrupole moment is a parameter which describes the effective shape of the ellipsoid of nuclear charge distribution. A non-zero quadrupole moment Q indicates that the charge distribution is not spherically symmetric. By convention, the value of Q is taken to be positive if the ellipsoid is prolate and negative if it is oblate.
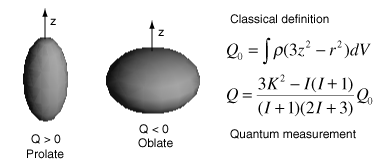
The quantity Q0 is the classical form of the calculation represents the departure from spherical symmetry in the rest frame of the nucleus. The expression for Q is the quantum mechanical form which takes takes into account the nuclear spin I and the projection K in the z-direction.
One of the expectations of the shell model for the nucleus is that for closed shells the nuclear charge is spherically symmetric. If a nucleus is not spherically symmetric, it will have a non-zero electric quadrupole moment, so the measurement of the quadrupole moment is a test of the shell theory. Since the quadupole moment depends upon the size and charge of the nucleus, a better comparison is obtained by normalizing for those factors, giving what is called a "reduced quadrupole moment". A plot of measured values shows that magic numbers of neutrons or protons correlate with near-zero quadrupole moments.
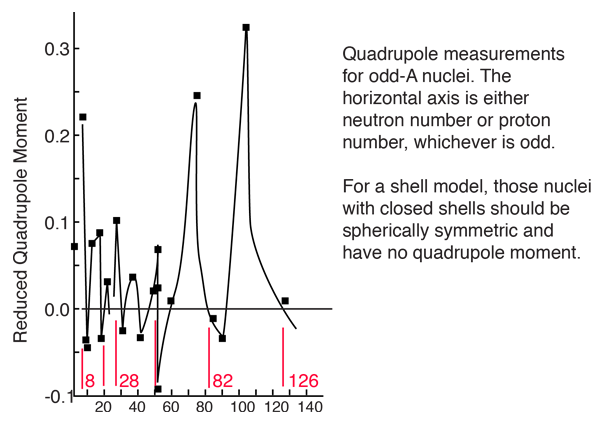
Electric quadrupole moments of nuclei can be measured brom hyperfine splitting of atomic spectral lines, from quadrupole hyperfine splitting of molecular rotational spectra, and other spectroscopic techniques.
| The electric quadrupole moment has the units of Coulomb x meter2. It is sometimes tabulated in units of e x 10-24 cm2 where e is the electron charge. In nuclear cross-section measurements, the quantity 10-24 cm2 is called a "barn" and is represented by b. So sometimes the quadrupole unit is written "eb" for electron-barns. Usually the quadrupole moments will be a few tenths in these units until you reach mass numbers around 150. Then quadrupole moments around 2 are common and have been measured as high as 8. Data from V. S. Shirley, Table of Isotopes, Wiley, New York, 1978, Appendix VII. |
| Evidence for nuclear shell structure | "Magic numbers" of nucleons |
Nuclear Structure Concepts
References
Booth & Combley
Krane
Ch 3
| HyperPhysics***** Nuclear | R Nave |