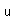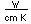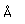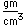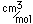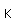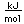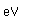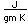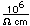Silicon
Silicon is a brittle steel-gray metalloid. In elemental form it has the same structure as diamond, each silicon forming single covalent bonds with four adjacent silicon atoms which surround it tetrahedrally.
Silicon chemistry is a vast area of study. Silicon is a constituent of many of the minerals which make up the earth's crust. Silicon is one of the big 8 elements in the Earth's crust, being the second most abundant element at about 27.7% by weight. The silicate minerals make up the vast majority of rocks found on the surface of the Earth.
Silicon as a semiconductor is the basis for solid state electronics, with electronic components being constructed primarily from doped silicon materials.
|