Velocity
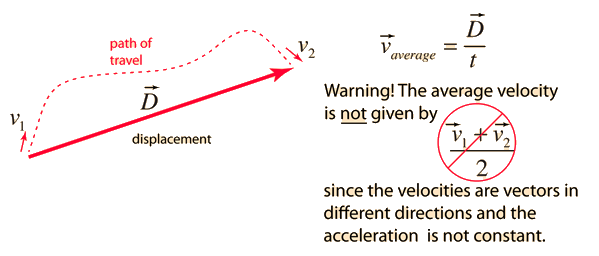
The average speed of an object is defined as the distance traveled divided by the time elapsed. Velocity is a vector quantity, and average velocity can be defined as the displacement divided by the time. For the special case of straight line motion in the x direction, the average velocity takes the form:
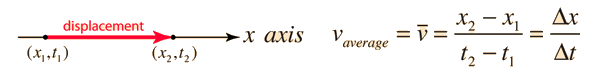
The units for velocity can be implied from the definition to be meters/second or in general any distance unit over any time unit.
You can approach an expression for the instantaneous velocity at any point on the path by taking the limit as the time interval gets smaller and smaller. Such a limiting process is called a derivative and the instantaneous velocity can be defined as

| Average velocity, straight line motion | Average velocity, general case |
Motion concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |