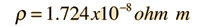AWG wire
size (solid) | Area
CM* | Resistance per
1000 ft (ohms) @ 20 C | Diameter
(inches) | Maximum current**
(amperes) |
| 0000 | 211600 | 0.049 | 0.46 | 380 |
| 000 | 167810 | 0.0618 | 0.40965 | 328 |
| 00 | 133080 | 0.078 | 0.3648 | 283 |
| 0 | 105530 | 0.0983 | 0.32485 | 245 |
| 1 | 83694 | 0.124 | 0.2893 | 211 |
| 2 | 66373 | 0.1563 | 0.25763 | 181 |
| 3 | 52634 | 0.197 | 0.22942 | 158 |
| 4 | 41742 | 0.2485 | 0.20431 | 135 |
| 5 | 33102 | 0.3133 | 0.18194 | 118 |
| 6 | 26250 | 0.3951 | 0.16202 | 101 |
| 7 | 20816 | 0.4982 | 0.14428 | 89 |
| 8 | 16509 | 0.6282 | 0.12849 | 73 |
| 9 | 13094 | 0.7921 | 0.11443 | 64 |
| 10 | 10381 | 0.9989 | 0.10189 | 55 |
| 11 | 8234 | 1.26 | 0.09074 | 47 |
| 12 | 6529 | 1.588 | 0.0808 | 41 |
| 13 | 5178.4 | 2.003 | 0.07196 | 35 |
| 14 | 4106.8 | 2.525 | 0.06408 | 32 |
| 15 | 3256.7 | 3.184 | 0.05707 | 28 |
| 16 | 2582.9 | 4.016 | 0.05082 | 22 |
| 17 | 2048.2 | 5.064 | 0.04526 | 19 |
| 18 | 1624.3 | 6.385 | 0.0403 | 16 |
| 19 | 1288.1 | 8.051 | 0.03589 | 14 |
| 20 | 1021.5 | 10.15 | 0.03196 | 11 |
| 21 | 810.1 | 12.8 | 0.02846 | 9 |
| 22 | 642.4 | 16.14 | 0.02535 | 7 |
| 23 | 509.45 | 20.36 | 0.02257 | 4.7 |
| 24 | 404.01 | 25.67 | 0.0201 | 3.5 |
| 25 | 320.4 | 32.37 | 0.0179 | 2.7 |
| 26 | 254.1 | 40.81 | 0.01594 | 2.2 |
| 27 | 201.5 | 51.47 | 0.0142 | 1.7 |
| 28 | 159.79 | 64.9 | 0.01264 | 1.4 |
| 29 | 126.72 | 81.83 | 0.01126 | 1.2 |
| 30 | 100.5 | 103.2 | 0.01002 | 0.86 |
| 31 | 79.7 | 130.1 | 0.00893 | 0.7 |
| 32 | 63.21 | 164.1 | 0.00795 | 0.53 |
| 33 | 50.13 | 206.9 | 0.00708 | 0.43 |
| 34 | 39.75 | 260.9 | 0.0063 | 0.33 |
| 35 | 31.52 | 329 | 0.00561 | 0.27 |
| 36 | 25 | 414.8 | 0.005 | 0.21 |
| 37 | 19.83 | 523.1 | 0.00445 | 0.17 |
| 38 | 15.72 | 659.6 | 0.00396 | 0.13 |
| 39 | 12.47 | 831.8 | 0.00353 | 0.11 |
| 40 | 9.89 | 1049 | 0.00314 | 0.09 |
|
The U.S. wire gauges (called AWG gauges) refer to sizes of copper wire. This table corresponds to a resistivity of 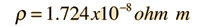 for copper at 20 C. This table uses this value of resistivity, but it is known to vary by a few percent based on purity and process of manufacture.
*The AWG system states areas of round copper wires in "circular mils", which is the square of the diameter in mils. 1 mil =.001 inch.
This data from Floyd, Electric Circuit Fundamentals, 2nd Ed.
**Maximum current for chassis wiring. Data from Handbook of Electronic Tables and Formulas for American Wire Gauge. The maximum current for power transmission is less.
|